
Micro- incision Cataract surgery (phacoemulsification)
A cataract is the clouding of the natural crystalline lens and typically occurs because of aging, although other reasons may be prolonged use of steroids, exposure to ultraviolet, and associated health problems like diabetes and eye injuries. Surgery is the only known effective treatment for cataract removal. All cataract surgeries are aimed at the removal of the cloudy natural lens and replacing it with an Intraocular Lens (IOL).
Lasik
LASIK stands for Laser in Situ Keratomileusis, which means using a laser underneath a corneal flap (in situ) to reshape the cornea (keratomileusis). This procedure utilizes a highly specialized laser (excimer laser) designed to treat refractive errors, improve vision, and reduce or eliminate the need for glasses or contact lenses. This laser procedure alters the shape of the cornea, which is the transparent front covering of the eye. Though the excimer laser had been used for many years before, the development of LASIK is generally credited to Ioannis Pallikaris from Greece around 1991.
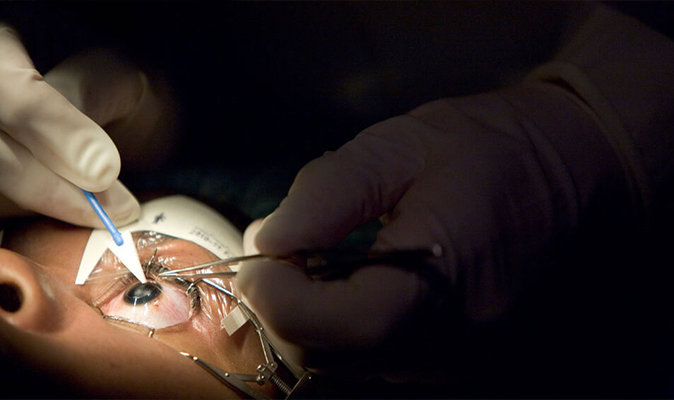
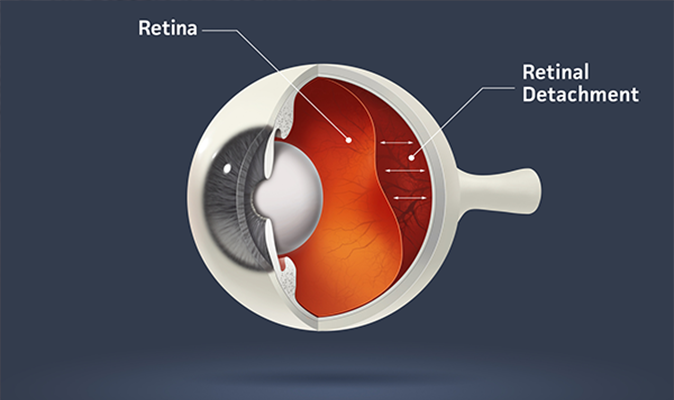
Evaluation & treatment of retinal diseases
Retina is the neurosensory layer of the eye which is present inside and at the back of the eye. It is on this layer that an image seen by the eye is formed, which is converted to nerve signals and transferred to the brain. Hence person with a normal eye but with a retina disease will have poor vision. The common diseases affecting retina are Diabetic Retinopathy and Retinal Detachment.
Glaucoma screening & Management
Glaucoma also called as Silent thief of sight is an asymptomatic disease of the eye that exhibits a typical optic neuropathy which results in progressive visual field loss. The most important risk factor is raised intraocular pressure. Risk factors for glaucoma include age above 40 years, diabetes, myopia, mature cataract, trauma, certain retinal diseases and a family history of glaucoma.
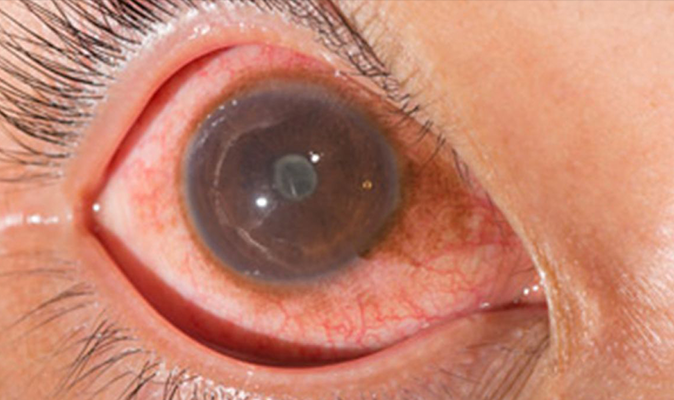
Uvea & Ocular inflammation management
The uvea plays an important role in the normal functioning of the eye. The iris, the ciliary body, and the choroid are called the uvea. The iris provides the eye with oxygen and nutrients; it acts as a shutter, controlling the amount of light entering the eye, and also contains muscles that help the eye to focus.
Uveitis is the inflammation of any part of the uvea and the symptoms are light sensitivity, blurring of vision, pain, redness of the eye, and floaters. Causes of uveitis include infections, auto-immune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, ankylosing spondylitis, Reiter’s disease, etc, severe injury to the other eye, and also due to some unknown causes.
Cornea & Ocular surface diseases
Corneal diseases can cause clouding and distortion of vision, and eventually blindness. There are many types of corneal diseases and infections such as bacterial, fungal, and viral infections related to contact lenses, abrasions from trauma, and inflammation, all of which need early treatment for the preservation of vision.


Squint a Pediatric Ophthalmology services
Pediatric ophthalmology is a subspecialty of ophthalmology that concerns vision care in children. Since the visual system is in a developing phase in childhood, hence it is imperative that any eye disorder in children be identified and rectified, as early as possible. Pediatric ophthalmologists treat eye defects in children through medication, therapies, and complex eye surgeries. Due to their expertise in handling eye movement disorders, pediatric ophthalmologists also treat squints in adults.

